
STDS TESTS
WHAT ARE SEXUAL TRANSMISSIONS?
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs or Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)) are diseases that are spread primarily through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Some STIs can also be spread through non-sexual means such as through blood or blood products. Many sexually transmitted diseases - including syphilis, hepatitis B, HIV, chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes and HPV - can also be passed from mother to baby during pregnancy and delivery. STIs have a profound impact on sexual and reproductive health worldwide. According to the WHO report, more than 1 million STIs are acquired every day, with an estimated 376 million new cases of 1 in 4 curable sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, gonorrhoea, trichomoniasis, syphilis) in 2016. .
Common symptoms of an STI include vaginal discharge, urethral discharge or burning in men, genital ulcers, and abdominal pain. However, some people can have an STI without having obvious symptoms of the disease [1]. As a result, they go undetected and untreated until complications arise. The consequences of untreated STIs are often more severe in women, including: infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pain, cervical cancer, and other complications. Early screening, diagnosis, counseling, and treatment can stop the spread of STIs and minimize complications.
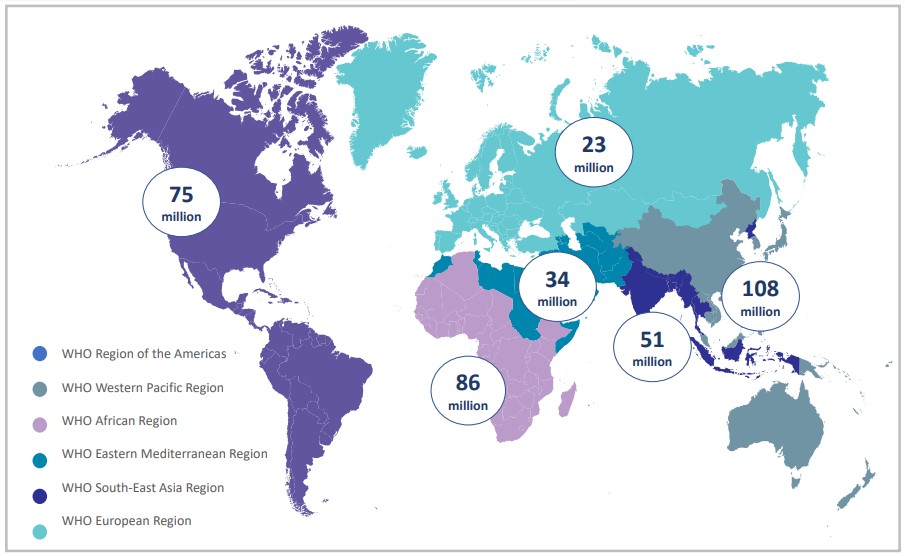
*Age from 15 to 49 years old. Source: Rowley J, et al. WHO Bulletin, 2019.
CAUSES OF DISEASE
Sexually transmitted diseases are caused by two main groups of agents, viruses and bacteria. Here are 12 common triggers that are commonly found.
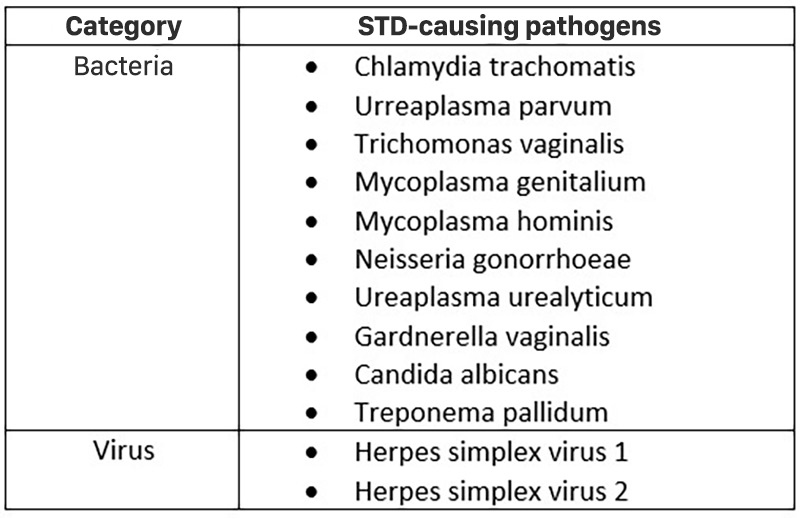
Sexually transmitted agents can cause many types of infections and the basic symptoms in men are pus discharge, abnormal urethral discharge, acute urethritis, etc. In women, it will cause neck inflammation. uterus, inflammation of 2 appendages, abnormal vaginal discharge, etc.
Among the pathogens found, chlamydia and gonorrhea are important causes of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and infertility. Without prompt treatment, about 10-15% of women with chlamydia will develop PID. Chlamydia can also infect the fallopian tubes without causing any symptoms. PID and “silent” infections of the upper genital tract can cause permanent damage to the fallopian tubes, uterus, and surrounding tissues, possibly leading to infertility. According to the CDC, in the United States, an estimated 4 million new chlamydia infections and 1.6 million new gonorrhea infections occurred in 2018 alone.
In particular, most women with chlamydia or gonorrhea have no symptoms. In addition, the CDC recommends annual gonorrhea and chlamydia screening for all sexually active women under age 25, as well as older women with risk factors such as new or multiple sex partners, or sexually transmitted infections.
EFFECTS OF STD
A sexually transmitted disease (STD) is a disease that is spread primarily through sexual contact, through blood, or from mother to child...
Common symptoms: vaginal discharge, urethral or burning sensation, itching genital sores, abdominal pain...
However, some people have no obvious symptoms, causing serious consequences: Infertility in both men and women, ectopic pregnancy, cervical cancer...
Screening, diagnosis right away for advice and early treatment. This can prevent the spread of STDs and reduce complications.
- More than 1 million STIs are acquired every day, of which the majority are asymptomatic.
- Each year, there are approximately 374 million new cases of 1 of the 4 common STIs: chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis and trichomoniasis.
- Over 500 million people (15 - 49 years old) are living with genital HSV (2016) infection and an estimated 300 million women are infected with HPV, the main cause of cervical cancer and anal cancer in men who have sex with men.
- Nearly 1 million pregnant women have syphilis, leading to more than 350,000 cases of adverse reproductive outcomes (2021).
- Sexually transmitted diseases such as herpes, gonorrhea and syphilis can increase the risk of HIV infection.
- STDs such as gonorrhea and chlamydia are major causes of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and infertility in women.
- Drug resistance is a major threat to reducing the global burden of STIs.
STD TEST VALUE
Support for doctors:
- Timely detection of STDs, helping doctors have the right treatment plan
- Screening for common and potential STDs
- Help doctors find the cause of male infertility due to infection with STDs
STDS TESTING IN GENTIS
STD testing at GENTIS supports the identification of 12 pathogens that cause STDs: Chlamydia trachomatis; Ureaplasma parvum; Trichomonas vaginalis; Mycoplasma genitalium; Mycoplasma hominis; Neisseria gonorrhoeae; Ureaplasma urealyticum; Gardnerella vaginalis; Candida albicans; Treponema pallidum; Herpes simplex virus 1; Herpes simplex virus 2.
- Sample usage:
- Vaginal smear (for women)
- Samples of pus, urethral fluid (for men)
- First-line urine sample (for men and women)
Sampling can be done by a qualified obstetrician-gynecologist or by yourself using an HPV self-collection kit. Store samples at room temperature for 24 to 48 hours. If more than 48 hours, store at 2-8oC (maximum no more than 7 days).
- Method:
Realtime-PCR technology to detect the presence and quantification of bacterial DNA in urine samples, urethral fluid, vaginal swabs using the IVD certified PANA RealTyper™ STD kit (PANAGENE) (PCR machine image)
- Time to return results: in 2-3 days
Please fill in the information below to receive our supports and consultations!







