
CFTR GEN MUTATION
WHAT IS CFTR GEN?
- The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 7 (7q31) (1).
- The CFTR gene encodes the CFTR protein, which acts as an ion channel on epithelial cells, with an important function in the regulation of ion transport across cell membranes, especially in the exocrine glands of the respiratory system. exocrine pancreas, digestive system and male reproductive system (2).
- The pathogenic mechanism of this mutation is autosomal recessive inheritance.
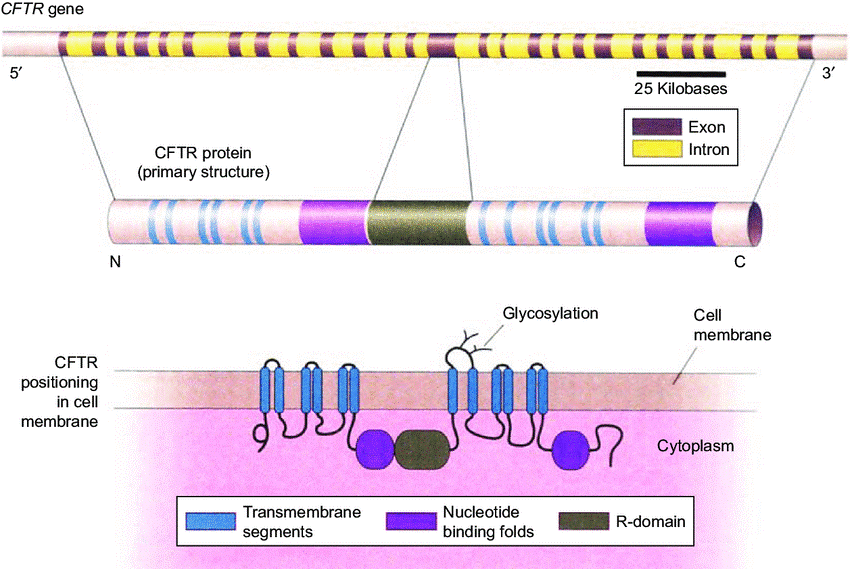
EFFECTS OF CFTR GENE MUTATIONS
Mutations in the CFTR gene result in quantitatively or qualitatively inefficient production of the CFTR protein, disrupting membrane ion transport, leading to a series of subsequent abnormalities. Common clinical symptoms:
- Imbalance of ions inside and outside the epithelial cell membrane in the exocrine glands, causing the exocrine fluid to have abnormal mucus, causing complicated symptoms, often in the respiratory and digestive systems (lung infections). recurrent, meconium bowel obstruction, constipation, etc.). This is the typical cause and symptoms of cystic fibrosis (CF). Cystic fibrosis affects approximately 1/3500 live births (European population) (2)
- Affects signal transduction pathways of male reproductive system formation and spermatogenesis, causing male infertility, most of which are due to congenital bilateral absence of vas deferens – CBAVD) (up to 97-98% in male CF patients) (3). Systematic reviews and analyzes indicate that up to 78% of CBAVD patients have one mutation in the CFTR gene, 53% have two, and 25% have only one mutation (2), (3). CFTR mutations were also found at an unusually high rate in the group of infertile men without CBAVD, with manifestations of oligospermia, sperm abnormalities… (2), (4).
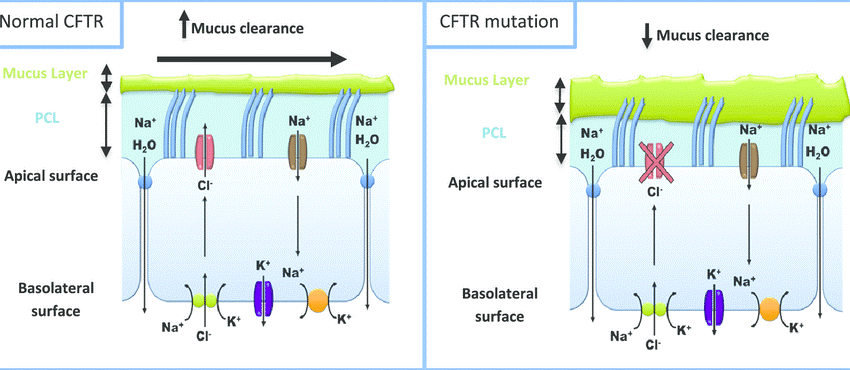
=>>> According to statistics, CFTR gene mutations appear in:
- 78% of patients with congenital bilateral vasectomy;
- 46% of unilateral vas deferens;
- 34-47% of epididymis obstruction of unknown cause;
- Can be found in male impotent azoospermia.
Symptoms of carriers of CFTR mutations vary widely, even among carriers of the identical CFTR genotype. This is due to variation related to the quality and quantity of protein expressed from person to person. Therefore, heterozygous carriers of mutations still have the potential to cause atypical symptoms of cystic fibrosis or male infertility, with many studies demonstrating (5).
Disease manifestations in CFTR mutation carriers are variable depending on the type of mutation. Based on the action of the CFTR protein, it can be divided into 6 types of mutations (6):
- Type I: does not produce CFTR Protein, typically mutant
- Type II: produces protein but fails to mature
- Type III: mature protein but fails to function
- Type IV: reduced ion channel transport function
- Type V: reduced production of CFTR proteins
- Type VI: reduced protein stability
Type I, II, III mutations are serious mutations, often causing typical symptoms of cystic fibrosis, male infertility, most commonly: Phe508Del, Asn1202Lys, Trp1282Ter, Gly542Ter...
CFTR GENE MUTATION TEST AT GENTIS
About 1500 mutations in the CFTR gene have been found, but not all mutations cause disease. Usually the identification of CFTR mutations is indicative of the presence or absence of common pathogenic mutations. A variety of mutations are used for routine diagnosis of mutation carriers and for prenatal and postnatal screening.
- CFTR gene test examines 22 common mutations: Gly542Ter, Trp1282Ter, Glu92Lys, 1677delTA, Lys68Glu, 2789+5G>A , Phe508del, 1717-1G>A, 4010delTATT, Phe1052Val, Ile148Thr, Gly551Asp, Tyr1032Cy 10kbC>T, Arg560Thr, 2183AA--G, Ser4Ter, Asn1303Lys, Val470Met, IVS8(T)n and (TG)m, Arg117His.
- Methods used:
The test uses DNA extraction from peripheral blood samples, then performs 2 methods to assess the status of mutations:
- Realtime PCR method evaluated 18 mutations: Gly542Ter, Trp1282Ter, Glu92Lys, 1677delTA, Lys68Glu, 2789+5G>A, Phe508del, 1717-1G>A, 4010delTATT, Phe1052Val, Ile148Thr, Gly551Asp, Tyr1032Cys, 3849 , Arg560Thr, 2183AA--G, Ser4Ter, Asn1303Lys
Sanger sequencing method to evaluate 2 mutations Val470Met, Arg117His, and 2 polymorphisms (T)n and (TG)m of IVS8
- The test examines the status of 20 common CFTR gene mutations: no mutation, heterozygous mutation, or homozygous mutation.
Simultaneously, the test investigates the repeatability (T)n polymorphism of the amino acid T (5T/7T/9T) and the repeat (TG)m of the two amino acids TG (11TG/12TG/13TG) located on the intron region. 8 (IVS8) of the CFTR gene.

SUBJECTS NEED TO TEST US
According to the European CFTR-related practice guidelines (2008) (7) and the Cystic Fibrosis Society Practice Guidelines (2017) (8), CFTR gene testing is indicated in cases of:
Subjects suspected of having cystic fibrosis:
- Patients with typical or atypical cystic fibrosis symptoms
- People with positive cystic fibrosis screening results with sweat chloride test
Objects of assisted reproduction:
- Male infertility due to idiopathic obstruction, vas deferens or vas deferens
- Men with low semen volume (<2ml) or pH <7.2, no or reduced fructose concentration, etc.
- Married women carrying the CFTR mutated gene
- Couples with a family history of cystic fibrosis or carriers of the CFTR CHI gene
=> The specific identification of CFTR gene mutations plays an important role for doctors in:
- Provide an accurate diagnosis for patients with cystic fibrosis, have a plan to use appropriate drugs (each type of mutation has different drugs),
- Provide specific exploration and treatment options (vasectomy/testicular biopsy, IVF...) for male infertility patients.
- Genetic counseling with disease carriers or mutation carriers.
TESTING PROCESS IN GENTIS
- Step 1: Take customer samples
Collect peripheral blood samples into sterile EDTA anticoagulant tubes, each tube contains 2-3ml of blood, each patient takes 1 blood tube. Ensure the principle of sterility when taking blood, ensure the order of blood collection tubes as prescribed.
Amniotic fluid sampling: cultured amniotic fluid, or DNA separated from cultured amniotic fluid.
- Step 2: Store samples at 4 – 8oC for 1-2 days, or at -20oC for 2-10 days.
- Step 3: Transfer samples to GENTIS testing center
- Step 4: Return results to customers in 5-7 days
1 - Jared M. Bieniek, Craig D. Lapin, Keith A. Jarvi. Genetics of CFTR and male infertility. Translational Andrology and Urology. 2020;10(3):1391-1400.
2 - Hui Chen, Ye Chun Ruan, Wen Ming Xu et al. Regulation of male fertility by CFTR and implications in male infertility. Human Reproduction Update. 2012;18(6):703-713.
3 - J. Yu, Z. Chen, Y. Ni et al. CFTR mutations in men with congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD): a systemic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod. Jan 2012;27(1):25-35.
4 - S. Gallati, S. Hess, D. Galié-Wunder et al. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator mutations in azoospermic and oligospermic men and their partners. Reprod Biomed Online. Nov 2009;19(5):685-94.
5 - J. M. Bieniek, C. D. Lapin, K. A. Jarvi. Genetics of CFTR and male infertility. Transl Androl Urol. Mar 2021;10(3):1391-1400.
6 - S. V. Pereira, J. D. Ribeiro, A. F. Ribeiro et al. Novel, rare and common pathogenic variants in the CFTR gene screened by high-throughput sequencing technology and predicted by in silico tools. Apr 17 2019;9(1):6234.
7 - E. Dequeker, M. Stuhrmann, M. A. Morris et al. Best practice guidelines for molecular genetic diagnosis of cystic fibrosis and CFTR-related disorders--updated European recommendations. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. Jan 2009;17(1):51-65.
8 - Philip M. Farrell, Terry B. White, Clement L. Ren et al. Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis: Consensus Guidelines from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. J Pediatr. 2017;181S:S4-S15.
Please fill in the information below to receive our supports and consultations!







