False POSITIVE IN NIPT TEST
Non-invasive prenatal screening test (NIPT) helps to screen for common fetal malformations through the analysis of fetal cfDNA released into the mother's blood with high accuracy and absolute safety. Figure 1). The NIPT test has been shown to be clinically effective with more than 99% accuracy, as evidenced by the increasing use of NIPT over the past decade and has become an indispensable prenatal screening test in clinical practice in many countries around the world.
The advent and rapid advancement of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have increased the accuracy of the method. However, NIPT remains a screening test, and if the results are high-risk, confirm the results with an invasive diagnostic test. There are many factors that affect the accuracy of the NIPT test, including biological factors.
Cases of discrepancy between NIPT results and diagnosis, although few, have been reported by many research groups. Among them, a more common case is the false-positive NIPT result. Based on multiple meta-analyses, reported false positive rates range from 0.04% to 0.06% for trisomy 21, 18, and 13. Factors causing false positives in the NIPT test are known to be: placental mosaicism, abortive twin pregnancy, maternal malignancy, and maternal chromosomal mosaicism.
CAUSE OF False POSITIVE RESULTS IN NIPT TEST
1. Placenta mosaic
Mosaic is the presence of two or more cell lines with different sets of chromosomes in the same individual. Mosaic phenomenon accounts for about 1-2% in natural pregnancies and according to incomplete statistics, is higher in cases of assisted reproduction. However, mosaic accounts for up to 20% of cases where NIPT results and invasive diagnostic results are inconsistent.
In the case of placental mosaicism, also known as localized placental mosaicism, the placenta appears many abnormal cell lines with different chromosomes, while the fetus has a completely normal set of chromosomes. At this time, the NIPT test based on the analysis of cfDNA released from the placenta will give a positive NIPT result, but in fact the fetus is completely healthy. In this case, mosaic caused a false-positive NIPT result.
Reports have also highlighted a few cases of placental mosaicism that resulted in false-positive NIPT results. In the study of Agnese et al in 2022, the research team reported a case of a pregnant woman at 15 + 3 days of gestation who was advised to perform NIPT test, NIPT results showed a high risk of T21 with z-score. is 16.21.
To confirm a positive NIPT result, at 19 + 2 days of gestation, the pregnant woman conducts amniocentesis to perform QF-PCR and karyotype, the results do not detect abnormalities on chromosome 21. With this result, the pregnant woman was carefully consulted and explained by the doctor about the discrepancy between the NIPT results and the amniocentesis results.
2. Disappeared Twins
Dissolution of twins (VT), first described in 1976, is the disappearance of the embryo or gestational sac following fetal cardiac activity that has been observed in both fetuses in a twin pregnancy. The incidence of VT has been shown to range from 10% to 39% in IVF pregnancies, while the rate of spontaneous pregnancy VT is still unclear. Cases of VT have been reported to be associated with adverse perinatal outcomes as well as an increased incidence of fetal malformations.
The presence of VT can affect NIPT test results, studies have shown that cfDNA from aborted twins can still be present in the mother's plasma at least 8 weeks after the termination of pregnancy and possibly up to 15 weeks (Figure 2). We know that chromosomal abnormalities are a major cause of miscarriage, and trisomy can be the cause of VT, which in turn can lead to false-positive NIPT results.
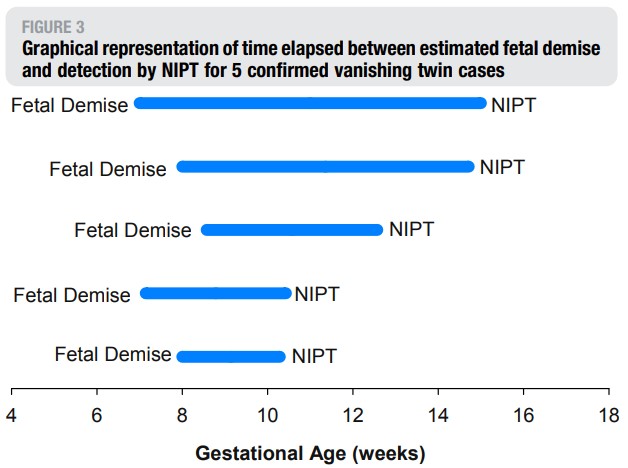
A recent study suggested that pregnant patients with VT should have a NIPT test 8 weeks after detection of VT. The study showed that, because the fetal fraction (FF) of VT was significantly reduced during these weeks and no longer affected NIPT results. However, this cannot be achieved when a woman's first obstetrician visit is too late to confirm pregnancy, a few weeks after the signs of twin pregnancy have disappeared. Therefore, it is recommended that pregnant women see their first obstetrician as soon as possible.
3. Malignancy in the mother
Maternal malignancy is relatively rare during pregnancy, with an incidence of 1 in 1000 pregnancies. In particular, according to statistics, breast cancer, liver cancer, lymphoma and stomach cancer are the most common cancers in pregnant women.
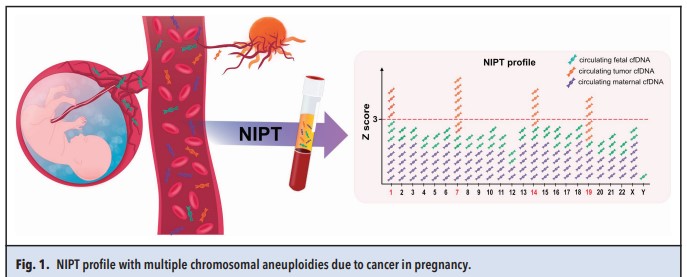
Studies have shown that underlying malignancies in the mother may provide a biological explanation for some of the contradictory NIPT results. Because cfDNA is released into the maternal circulation from programmed cell death (Figure 3).
These cfDNAs made the total maternal cfDNA increase, when the software compares with the reference sample and reads the results, it will easily give the NIPT result erroneous. If the mother's malignancy is not confirmed detected before pregnancy, this would be a contributing factor to false-positive NIPT results. In addition, there are also a few studies that report maternal malignancy through NIPT testing. Because one theory is that, when the risk of birth defects in the fetus is increased, there is a potential risk due to the occurrence of malignancy in the mother.
4. Mosaic chromosome in mother
Like maternal malignancy, maternal chromosomal mosaicism is also a factor in false-positive NIPT results with a similar principle. Maternal mosaicism can increase the amount of cfDNA in abnormal cells and in total cfDNA circulating in the maternal blood. If the mother's condition is not detected before pregnancy, the results may mistake the abnormality for the fetus.
Some recommendations are given to overcome this situation that pregnant women should be thoroughly examined before pregnancy as well as sharing about current medical conditions, family history is extremely important to Pregnancy management is carried out in the most favorable way.
Besides biological factors affecting NIPT test results, technical factors such as the technology platform used are also a factor affecting the accuracy of the test. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) technology on the NextSeq 550 sequencer system from Illumina, USA is a proven technology platform with more than 99% accuracy, less than 0.1% failure rate.
The data provided by Illumina suppliers is made on a large clinical database, and this is also a technology platform that is voted by the worldwide community of scientists as the technology company used in the field. Scientific research, development of tests in the field of molecular biology the most.
GENTIS is a genetic analysis unit in Vietnam that uses Illumina technology for NIPT testing. In addition, the GENTIS R&D team has successfully developed an advanced bioinformatics software that optimizes the readability of the results, thereby improving the accuracy of the NIPT test.
Although the NIPT test, although highly accurate, is still a screening test, factors that can lead to biased results have also been presented and reported. This again emphasizes the importance of more careful ultrasound and pregnancy monitoring to limit unwanted outcomes. Through the article, we hope that we have provided useful information to clinicians, thereby helping doctors have more timely and appropriate advice and indications for pregnant women.
References:
[1] van der Meij K. R. M., Sistermans E. A., Macville M. V. E., Stevens S. J. C., Bax C. J., Bekker M. N., et al. (2019). TRIDENT-2: National implementation of genome-wide non-invasive prenatal testing as a first-tier screening test in The Netherlands. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 105, 1091–1101. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.10.005
[2] Kleinfinger, Pascale et al. “Noninvasive Prenatal Screening for Trisomy 21 in Patients with a Vanishing Twin.” Genes vol. 13,11 2027. 3 Nov. 2022, doi:10.3390/genes13112027
[3] Gug, Cristina et al. “Genetic Counseling and Management: The First Study to Report NIPT Findings in a Romanian Population.” Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania) vol. 58,1 79. 5 Jan. 2022, doi:10.3390/medicina58010079
[4] Lenaerts, Liesbeth et al. “Noninvasive Prenatal Testing and Detection of Occult Maternal Malignancies.” Clinical chemistry vol. 65,12 (2019): 1484-1486. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2019.306548
[5] Snyder MW, Simmons LE, Kitzman JO, et al. Copy-number variation and false positive prenatal aneuploidy screening results. N Engl J Med 2015; 372:1639–45
[6] Grömminger, Sebastian et al. “Fetal Aneuploidy Detection by Cell-Free DNA Sequencing for Multiple Pregnancies and Quality Issues with Vanishing Twins.” Journal of clinical medicine vol. 3,3 679-92. 25 Jun. 2014, doi:10.3390/jcm3030679
[7] Grati, F R. “Implications of fetoplacental mosaicism on cell-free DNA testing: a review of a common biological phenomenon.” Ultrasound in obstetrics & gynecology: the official journal of the International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology vol. 48,4 (2016): 415-423. doi:10.1002/uog.15975











