
Preeclampsia
Overview
Preeclampsia is a multiorgan syndrome that develops in the second half of pregnancy, characterized by hypertension associated with albuminuria or multiple organ dysfunction.
- Hypertension is an increase in blood pressure after 20 weeks of pregnancy that increases continuously more than 2 times, 4 hours apart. Chronic hypertension in which the following factors are present is called overlapping preeclampsia, chronic hypertension.
- Signs to diagnose preeclampsia include:
Proteinuria: ≥300 mg of protein in 24-hour urine or protein/creatinine ratio ≥30 mg/mmol Renal failure: Blood creatinine 90 μmol/L mpaired liver function: Increased liver enzyme levels in the blood to 2 times the normal threshold or abnormal lower back pain Neurological complications: eclampsia, stroke, confusion, headache, temporary blindness, visual disturbances Blood complications: platelets <150,000/dL, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome or bleeding.
Epidemiology
- In Vietnam, a series of studies from 2012 to 2016 in Hue showed that about 2.8 - 5.5% of pregnant women had preeclampsia.
- Preeclampsia rate before 34 weeks is 0.43%, preeclampsia rate from 34 to 37 weeks is 0.70% and preeclampsia rate after 37 weeks is 1.68%.
- The rate of gestational hypertension is about 0.50%, this group of diseases usually has little effect on pregnancy, but about 15-25% of cases can progress to preeclampsia.
High-risk population
ACOG's recommendation:
| - Pregnant with a baby - Multiple pregnancy - History of pregnancy preeclampsia - Systemic lupus erythematosus - Hereditary hemophilia | - Chronic hypertension- Hereditary hemophilia - Body mass index (BMI) before pregnancy from over 35 kg/m2 - Antiphospholipid syndrome - Diabetes and gestational diabetes | - Pregnant mother from over 35 years old - Kidney disease - Use assisted reproduction methods - There is an obstructive sleep apnea |
According to ACOG's recommendations, these subjects should be identified as high-risk groups and need preventive treatment, however, if only following ACOG's recommendations, up to 50% of those who need to be treated can be missed. must be treated.
When should the test be taken
The current pregnancy management approach applies a pyramid model, in which determining the risk for complications later in pregnancy is the basis for developing an appropriate management plan.
Current evidence points to a two-stage screening model:
- Phase 1 at 11 weeks 0 days to 13 weeks 6 days (11-13+6) of pregnancy will focus on early preeclampsia screening and preventive intervention (FMF).
- Phase 2 in the second and third quarters, continued screening for both early preeclampsia and term preeclampsia for appropriate management of high-risk cases.
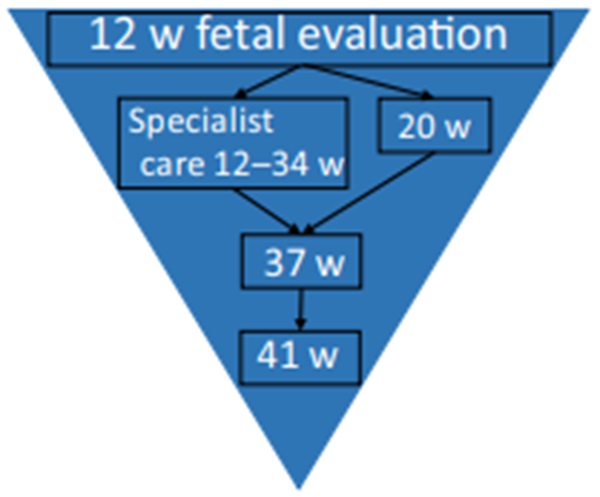
Management of preeclampsia
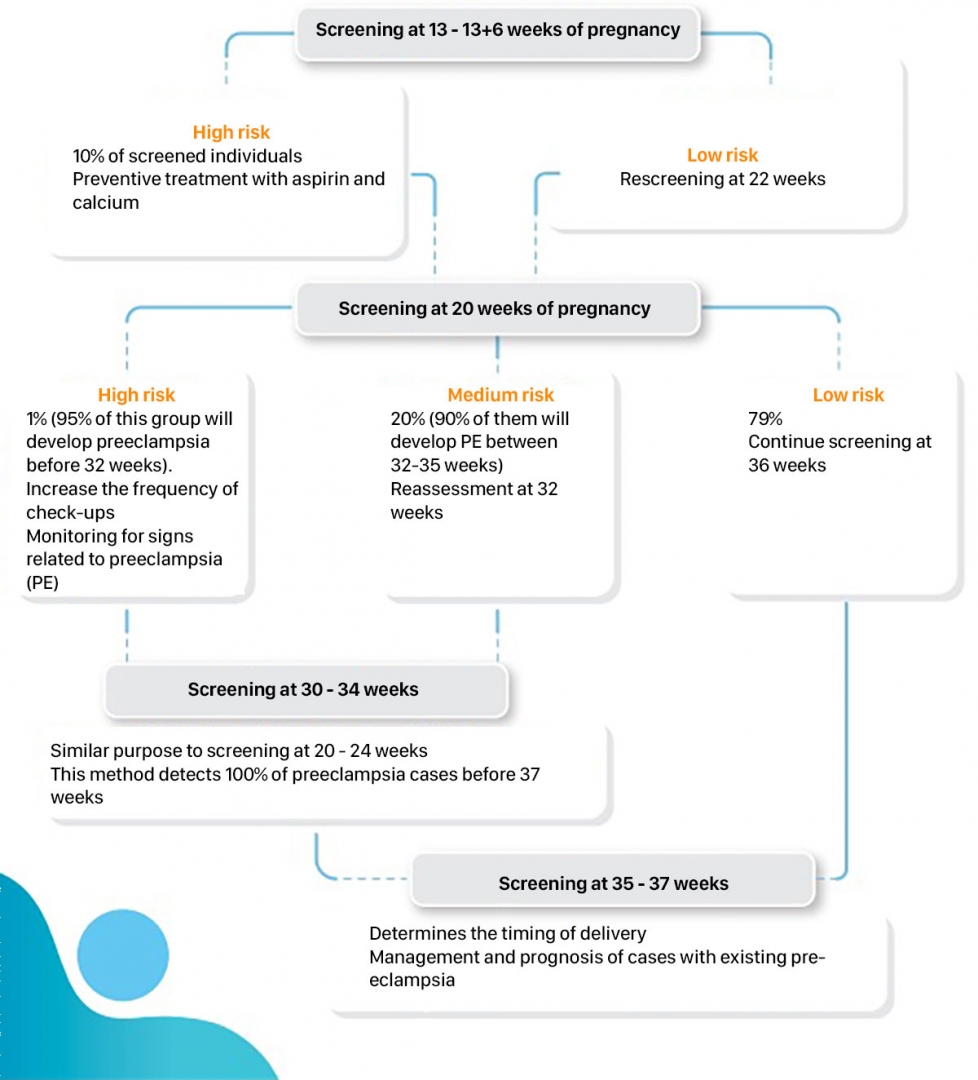
- Parameters related to the mother's history, ultrasound information, examination information will be combined to calculate the risk of preeclampsia in the mother.
- The ratio sFLT-1/PlGF has prognostic value in cases where it is necessary to predict complications of preeclampsia.
Testing at Gentis
- First trimester: PlGF index (from 10 to 13 weeks gestation) combined with maternal history, examination information and ultrasound results.
- The second and third trimesters: The ratio sFLT-1/PlGF predicts poor pregnancy outcomes of pregnant women (from the 19th week of pregnancy) combined with maternal history, examination information and ultrasound results.
- Sample: 2ml of peripheral blood
- Time to return results: 2 days
References
1. Rolnik, Daniel L. et al. Prevention of preeclampsia with aspirin Rolnik, Daniel L. et al. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Volume 0, Issue 0
2. Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 222. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jun;135(6):e237-e260.
3. Trần Mạnh Linh: nghiên cứu kết quả sàng lọc bệnh lý tiền sản giật - sản giật bằng xét nghiệm PAPP-A, siêu âm DOPPLER động mạch tử cung và hiệu quả điều trị dự phòng. 2020 – Đại học Y Dược Huế
Please fill in the information below to receive our supports and consultations!







