-
- 1800 2010
- EN

News
Array
(
[0] => stdClass Object
(
[id] => 1142
[id_crawler] =>
[category_product] => NULL
[thumbnail] => ht-sk_2023/sinh_nhật_cong_ty_2023/backdrop_sn_cong_ty_2023.jpg
[album] =>
[url_video] =>
[is_status] => 1
[is_featured] => 0
[is_form] => 0
[displayed_time] => 2023-10-09
[program] => 0
[number] => 1
[viewed] => 0
[type] =>
[type_career] =>
[level] =>
[address] =>
[address_career] =>
[expiration_time] => 0000-00-00
[created_time] => 2023-10-09 09:01:20
[updated_time] => 2024-08-19 13:53:19
[files] =>
[salary] =>
[time] =>
[created_by] => 62
[is_table_content] => 0
[language_code] => en
[slug] => gentis-13th-anniversary-strong-foundation-breakthrough-together
[title] => GENTIS 13th Anniversary: Strong Foundation - Breakthrough together
[description] => Through 13 years of dedication to our mission of enhancing the physical and intellectual well-being of Vietnamese people, GENTIS has become a trusted and reputable brand in Vietnam. Building on this strength, GENTIS embraces the spirit of "United and Thriving" this year to further develop and expand our company. Stay tuned for a series of special and impressive events to commemorate GENTIS's 13th anniversary.
[content] => 
Established on October 26, 2010, by a team of leading scientists in the fields of diagnostics and biotechnology, GENTIS has continuously grown to become a trusted name in genetic testing. We are proud to be a reliable partner of hospitals, clinics, and a trusted healthcare companion for Vietnamese families.
Moreover, GENTIS has become a second home to nearly 200 employees. With our united spirit and commitment to "Breakthrough together", the GENTIS team promises to deliver even more impressive achievements in the coming year.
To celebrate our 13th anniversary, all GENTIS employees are invited to join us in a series of exciting events throughout October.
Sales race (September 26 - October 24): Having revenue is having everything - Revenue is power. Four teams: Customer Service, Online Business HCM, Offline Business HN, Offline Business HCM are ready to participate in creating a breakthrough this October. The entire company will stand together, enthusiastically support and strongly cheer for all 4 highest winning racing teams.
3rd Annual Football Super Cup (Oct 15 - 22): A great opportunity to connect GENTIS with our partners and clients while showcasing our team spirit.
Men in Bloom (Oct 20): The first event appearing at GENTIS, this is not a playground for women but this is the "headquarters" for GENTIS men to express their creativity, skillful techniques to collectively create beautiful flower vases for GENTIS women.
Interdepartmental musical performance: Sweet or personality, gentle or hot, you don't have to choose because GENTIS-ers have them all. Rolling cultural performances have always been GENTIS's specialty for the past 13 years. Look forward to excellent performances with 3 inter-departmental entertainment teams at the gala night of October 25.
GENTIS Teambuilding + Gala Dinner: This is definitely an indispensable event at GENTIS: Fiery teambuilding and heroic GALA night are always long for and carefully prepared by all GENTIS employees.
Detailed information about GENTIS's 13th birthday celebration program will be continuously updated at the GENTIS Fan Page and website www.gentis.com.vn. Please look forward to it and join GENIS!
[content_more] =>
[meta_title] => GENTIS 13th Anniversary: Strong Foundation - Breakthrough together
[meta_description] => Through 13 years of dedication to our mission of enhancing the physical and intellectual well-being of Vietnamese people, GENTIS has become a trusted and reputable brand in Vietnam. Building on this strength, GENTIS embraces the spirit of "United and Thri
[meta_keyword] => GENTIS 13th Anniversary
[thumbnail_alt] =>
[post_id] => 1142
[category_id] => 4
)
[1] => stdClass Object
(
[id] => 1141
[id_crawler] =>
[category_product] => NULL
[thumbnail] => ht-sk_2023/san_nhi_na_30-9/trc_sk_na.png
[album] =>
[url_video] =>
[is_status] => 1
[is_featured] => 0
[is_form] => 0
[displayed_time] => 2023-09-27
[program] => 0
[number] => 1
[viewed] => 0
[type] =>
[type_career] =>
[level] =>
[address] =>
[address_career] =>
[expiration_time] => 0000-00-00
[created_time] => 2023-10-04 17:02:54
[updated_time] => 2024-08-16 14:49:45
[files] =>
[salary] =>
[time] =>
[created_by] => 62
[is_table_content] => 0
[language_code] => en
[slug] => gentis-is-the-official-partner-of-the-1st-regional-conference-on-prenatal-and-neonatal-diagnostic-screening-in-north-central-vietnam
[title] => GENTIS is the official partner of the 1st Regional Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Diagnostic Screening in North-Central Vietnam
[description] => On September 30, 2023, the Nghe An Department of Health, in partnership with the Nghe An Obstetrics and Pediatrics Hospital, will convene the 1st Regional Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Diagnostic Screening in North-Central Vietnam, which will be attended by numerous delegates from across the country. GENTIS is honored to be the silver sponsor of the Conference and will be showcasing the noteworthy products and testing services in the domain of prenatal and neonatal diagnostic screening.
[content] =>

The Conference is organized by the Nghe An Department of Health in collaboration with the Nghe An Obstetrics and Pediatrics Hospital, with the participation of the Representatives from the leadership of the General Office for Population and Family Planning; Representatives from the Department of Population Structure and Quality and relevant departments and units under the General Department; Specialists from Prenatal and Neonatal Diagnostic Screening Centers across the country, as well as experts from leading specialized hospitals such as the National Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology, National Children's Hospital, Tu Du Hospital, Children's Hospital 1, Hanoi Medical University Hospital, Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, and the Chinese University of Hong Kong, etc.
- Occurrence time: Saturday, September 30th, 2023.
- Location: Ballroom 2 - Giao Te Hotel, 9 Ho Tung Mau Street, Hung Binh Ward, Vinh City, Nghe An Province.
The Conference is poised to deliver a wealth of meaningful information and in-depth expertise on various prenatal and neonatal diagnostic screening methods.
GENTIS is honored to be the Silver Sponsor for this conference and will host an exhibitor booth to provide advisory services and introduce the latest genetic testing solutions in the domains of prenatal screening and obstetrics to the distinguished delegates in attendance.
Furthermore, when visiting the GENTIS booth, esteemed guests and delegates will have the chance to engage in many entertaining activities, including a lucky draw with a 100% opportunity of winning prizes. These prizes include books on Andrology, GENTIS-branded USB drives, phone stands, and other attractive giveaways.
We cordially invite all distinguished experts, physicians, and healthcare personnel to attend this conference!
[content_more] =>
[meta_title] => GENTIS is the official partner of the 1st Regional Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Diagnostic Sc
[meta_description] => On September 30, 2023, the Nghe An Department of Health, in partnership with the Nghe An Obstetrics and Pediatrics Hospital, will convene the 1st Regional Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Diagnostic Screening in North-Central Vietnam, which will be att
[meta_keyword] => Regional Conference
[thumbnail_alt] =>
[post_id] => 1141
[category_id] => 4
)
[2] => stdClass Object
(
[id] => 1140
[id_crawler] =>
[category_product] => NULL
[thumbnail] => ht-sk_2023/san_nhi_na_30-9/san-nhi-na-5-min.jpg
[album] =>
[url_video] =>
[is_status] => 1
[is_featured] => 0
[is_form] => 1
[displayed_time] => 2023-10-04
[program] => 0
[number] => 1
[viewed] => 0
[type] =>
[type_career] =>
[level] =>
[address] =>
[address_career] =>
[expiration_time] => 0000-00-00
[created_time] => 2023-10-04 15:42:56
[updated_time] => 2024-08-19 13:49:18
[files] =>
[salary] =>
[time] =>
[created_by] => 62
[is_table_content] => 1
[language_code] => en
[slug] => gentis-is-honored-to-be-the-silver-sponsor-of-the-1st-north-central-region-conference-on-prenatal-and-eonatal-screening-and-diagnosis
[title] => GENTIS is honored to be the Silver Sponsor of the 1st North Central Region Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Screening and Diagnosis
[description] => On September 30th, 2023, GENTIS proudly supported the 1st North Central Region Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Screening and Diagnosis, held at Nghe An Maternity and Children's Hospital, bringing together nearly 500 domestic and international medical professionals. As a Silver Sponsor, GENTIS was honored to contribute to the success of this important event.
[content] => The 1st North Central Region Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Screening and Diagnosis was held on September 30th, 2023, at Hall 2 of Giao Te Hotel, 9 Ho Tung Mau Street, Hung Binh Ward, Vinh City, Nghe An Province. The event was co-organized by the Department of Health of Nghe An Province and Nghe An Maternity and Children's Hospital.
 The 1st North Central Region Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Screening and Diagnosis attracted nearly 500 domestic and international medical professionals and experts
The 1st North Central Region Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Screening and Diagnosis attracted nearly 500 domestic and international medical professionals and experts
This prestigious conference provided obstetricians, gynecologists, prenatal diagnosis specialists, and neonatal care providers with an opportunity to exchange knowledge, enhance their professional skills, and contribute to the development of Vietnam's healthcare system, particularly in the fields of obstetrics, gynecology, and pediatrics.
A total of 25 papers were presented by leading domestic and international professors, doctors, and experts from countries with advanced medicine. These presentations focused on timely topics and shared in-depth knowledge and the latest advancements in prenatal and neonatal diagnosis and screening, including aneuploidy screening, premature infant care, fetal echocardiography, genetic sequencing, gene mutations, and NIPT testing.
 The conference featured 25 papers delivered by leading domestic and international professors, doctors, and experts
The conference featured 25 papers delivered by leading domestic and international professors, doctors, and experts
GENTIS was honored to be a Silver Sponsor of this significant conference and had an exhibition booth. Our booth attracted a large number of doctors, nurses, and technicians. In particular, healthcare professionals highly appreciated GENTIS's tests, especially GenEva NIPT, Hemophilia, Karyotype, the 13 hidden diseases combo, and newborn screening,...
 GENTIS's exhibition booth was a major draw for conference delegates and guests
GENTIS's exhibition booth was a major draw for conference delegates and guests
In addition to providing product and service consultations, GENTIS organized engaging mini-games that not only updated participants on our testing services but also offered valuable prizes such as gynecology books, GENTIS USB drives, and phone holders. The GENTIS booth left a positive impression and contributed to the vibrant atmosphere of the conference.
 Guests had the opportunity to participate in engaging mini-games and receive valuable gifts from GENTIS
Guests had the opportunity to participate in engaging mini-games and receive valuable gifts from GENTIS
In addition, GENTIS was honored to provide information on NIPT testing for Nguyen Khac Han Hoan M.D, PhD in his presentation titled "Clinical Factors Affecting the Accuracy of NIPT."
Nguyen Khac Han Hoan M.D, PhD's presentation clarified important factors that ensure the accuracy of non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPT), such as the ratio of fetal cfDNA in maternal blood, vanishing twins with residual fetal cfDNA, mosaicism in the placenta and fetus, and maternal organ transplantation.
 Nguyen Khac Han Hoan M.D, PhD presented on the topic "Clinical Factors Affecting the Accuracy of NIPT."
Nguyen Khac Han Hoan M.D, PhD presented on the topic "Clinical Factors Affecting the Accuracy of NIPT."
As a pioneer in genetic analysis in Vietnam, GENTIS utilizes Illumina technology for NIPT testing. Additionally, GENTIS's R&D team has successfully developed an advanced bioinformatics software to optimize result interpretation, thereby enhancing the accuracy of NIPT.
The 1st North Central Region Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Screening and Diagnosis was a resounding success. The event provided a valuable platform for doctors and experts to network, exchange knowledge, and acquire in-depth expertise in prenatal and neonatal screening and diagnosis. GENTIS would like to once again congratulate the conference on its great success.
[content_more] =>
[meta_title] => GENTIS is honored to be the Silver Sponsor of the 1st North Central Region Conference on Prenatal an
[meta_description] => On September 30th, 2023, GENTIS proudly supported the 1st North Central Region Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Screening and Diagnosis, held at Nghe An Maternity and Children's Hospital, bringing together nearly 500 domestic and international medical
[meta_keyword] => North Central Region Conference
[thumbnail_alt] =>
[post_id] => 1140
[category_id] => 4
)
[3] => stdClass Object
(
[id] => 1139
[id_crawler] =>
[category_product] => NULL
[thumbnail] => hoi-nghi-acp-2023.jpg
[album] =>
[url_video] =>
[is_status] => 1
[is_featured] => 0
[is_form] => 1
[displayed_time] => 2023-10-03
[program] => 0
[number] => 1
[viewed] => 0
[type] =>
[type_career] =>
[level] =>
[address] =>
[address_career] =>
[expiration_time] => 0000-00-00
[created_time] => 2023-10-03 15:50:49
[updated_time] => 2024-08-16 13:39:13
[files] =>
[salary] =>
[time] =>
[created_by] => 63
[is_table_content] => 1
[language_code] => en
[slug] => gentis-the-main-sponsor-of-the-acp-2023-annual-scientific-conference
[title] => GENTIS - The Main Sponsor of the ACP 2023 Annual Scientific Conference
[description] => Recently, the Phuong Chau Medical Corporation organized the 2023 Annual Scientific Conference (ACP) with the theme "Enhancing Excellent Medical Experiences for the Community" at the CB Diamond Palace Convention Center (Can Tho City). GENTIS proudly participated as the Main Sponsor and showcased a product exhibition booth.
[content] => 
GENTIS washonored to be the main sponsor of the ACP 2023 Annual Scientific Conference
The ACP 2023 Annual Scientific Conference is a significant event organized by the Phuong Chau Medical Corporation, attracting over 1,000 delegates including leading experts, healthcare professionals, and staff from hospitals specializing in Obstetrics and Gynecology, Infertility, Pediatrics and Neonatology, General Medicine, Quality Management - Hospital Management, and Nursing from southern provinces and cities. This event provides an opportunity for professionals to interact, learn, and exchange knowledge and experience in the medical field.
This year's conference featured 48 reports on the most current topics in Obstetrics and Gynecology, Pediatrics, Infertility, General Medicine, Nursing, and Quality Management - Hospital Management. The reports were presented by senior hospital management leaders from the Phuong Chau Medical Corporation and leading experts from hospitals in the southern region.

GENTIS's product introduction booth attracted the attention of many delegates
A highlight of GENTIS's participation in the ACP 2023 Annual Scientific Conference was its product exhibition booth. Here, doctors and experts had the opportunity to explore the most comprehensive and modern genetic testing ecosystem and receive valuable gifts of gratitude. Leading experts highly praised GENTIS's tests, especially the NIPT, PGT Max 1 tests, etc,...

Many customers visited GENTIS's booth to receive gifts
Through our service introduction activities at the ACP 2023 Annual Scientific Conference, GENTIS hopes to continue partnering with doctors and experts in bringing genetic tests closer to the Vietnamese population.
[content_more] =>
[meta_title] => GENTIS - The Main Sponsor of the ACP 2023 Annual Scientific Conference
[meta_description] => Recently, the Phuong Chau Medical Corporation organized the 2023 Annual Scientific Conference (ACP) with the theme "Enhancing Excellent Medical Experiences for the Community" at the CB Diamond Palace Convention Center (Can Tho City). GENTIS proudly partic
[meta_keyword] =>
[thumbnail_alt] =>
[post_id] => 1139
[category_id] => 4
)
[4] => stdClass Object
(
[id] => 1136
[id_crawler] =>
[category_product] => NULL
[thumbnail] => ht-sk_2023/hn_di_truyen_thai_binh/wweb_chinh.png
[album] =>
[url_video] =>
[is_status] => 1
[is_featured] => 0
[is_form] => 1
[displayed_time] => 2023-10-03
[program] => 0
[number] => 1
[viewed] => 0
[type] =>
[type_career] =>
[level] =>
[address] =>
[address_career] =>
[expiration_time] => 0000-00-00
[created_time] => 2023-10-03 08:24:59
[updated_time] => 2024-08-15 16:28:38
[files] =>
[salary] =>
[time] =>
[created_by] => 63
[is_table_content] => 1
[language_code] => en
[slug] => GENTIS is honored to be the Main Sponsor of the 2023 National Scientific Conference of the Vietnam Medical Genetics Association.
[title] => GENTIS is honored to be the Main Sponsor of the 2023 National Scientific Conference of the Vietnam Medical Genetics Association.
[description] => The 2023 National Scientific Conference is an annual event organized by the Vietnam Medical Genetics Association, which will take place on October 6-7, 2023 at Thai Binh University of Medicine and Pharmacy. This year, GENTIS is honored to accompany the conference as the Main Sponsor.
[content] => This is an important activity of the Vietnam Medical Genetics Association, held once a year. This year's conference has the theme "Genetic Diagnosis, Prenatal and Newborn Screening", and is expected to attract more than 500 delegates, including doctors, experts and medical professionals in the field of genetics, obstetrics and gynecology, assisted reproduction, neonatal pediatrics and related specialties nationwide.

The conference’s agenda:
I. Continuing Medical Education Course: October 6, 2023: 2:00 PM - 3:30 PM
Topic: Clinical Cancer Genetics
II. Executive Board Meeting: October 6, 2023: 6:00 PM
- Gala dinner: 7:00 PM, October 6, 2023.
- LOCATION: Thai Binh Dream Hotel, No. 355 Ly Bon - 241 Hai Ba Trung, De Tham Ward, Thai Binh City
III. Official Conference on October 7, 2023: 8:15 AM - 5:15 PM
- Plenary Session: 8:30 AM - 10:30 AM: Hall 1
- 3 thematic Sessions: 40 scientific reports
+ Session 1: Cancer Genetics
+ Session 2: Cardiovascular and hematologic genetics, rare diseases
+ Session 3: Prenatal screening and diagnosis
- 30 poster presentations on medical genetics.
When attending this conference, doctors/partners should not miss the main activities of GENTIS:
- Exhibition booth, introducing products with many advanced gene testing documents, along with many valuable gifts for doctors and delegates.
- Booth No. 1, Thai Binh University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Thai Binh City
- GENTIS representative - Nguyen Thi Huyen, MSc. MD. - Genetic Analysis Services Joint Stock Company (GENTIS) will present a scientific report on Newborn Screening for Metabolic Disorders.
At the same time, GENTIS also provides information on tests for the report topics on genetic diagnosis, prenatal screening and newborn screening.
We look forward to welcoming you, delegates and doctors!
Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: A Comprehensive Overview
Recurrent pregnancy loss is characterized by the loss of three or more consecutive pregnancies prior to the 20th week of gestation (Ford, 2009), excluding ectopic, molar, and biochemical pregnancies. This condition affects approximately 1-2% of women of reproductive age and remains a significant clinical challenge (Stephenson, 1996).

Nevertheless, when recurrent pregnancy loss is defined as the loss of two or more consecutive pregnancies (ACOG, 2013), the incidence rises to 5%. The risk of subsequent pregnancy loss increases to 24% after two miscarriages, 30% after three miscarriages, and up to 40% after four consecutive miscarriages (Regan, 1989).
Etiologies of recurrent pregnancy loss included:
- Anatomical uterine abnormalities, infections
- Endocrine and immunological disorders
- Thrombophilia
- Genetic abnormalities
- Environmental factors and causes unknown
Thrombophilia, a heterogeneous group of inherited or acquired thrombophilic disorders, has emerged as a significant risk factor for recurrent pregnancy loss.
Classification of Thrombophilia
Thrombophilia is a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by an increased tendency of blood to clot. Both inherited and acquired thrombophilic states are prevalent. Approximately 15% of the Caucasian population carries a genetic mutation associated with a hypercoagulable state.

Classification of thrombophilia includes:
Inherited thrombophilia: Characterized by genetic mutations such as Factor V Leiden (FVL), prothrombin factor II G20210A gene mutation (FII), methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase mutation (MTHFR) leading to hyperhomocysteinemia, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) gene mutations.
Acquired thrombophilia: Including antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), protein S deficiency, and protein C deficiency.
Combined thrombophilia: A combination of inherited and acquired thrombophilic states, such as methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene (MTHFR) mutation in conjunction with folate and vitamin B12 deficiency.
Thrombophilia and Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
Recent research has focused on systematic reviews investigating the association between inherited thrombophilia and recurrent pregnancy loss, the role of thrombophilic gene polymorphisms, the efficacy of low-molecular-weight heparin, and the specific contributions of prothrombin G20210A mutation, Factor V Leiden mutation, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) gene polymorphisms to recurrent miscarriage.
Women with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss should undergo a comprehensive preconception evaluation 3-5 months prior to attempting conception. This evaluation should include a thorough medical history, physical examination, and appropriate laboratory investigations to identify and address underlying factors contributing to infertility or recurrent pregnancy loss.
Thrombophilia Testing at GENTIS

|
Thrombophilia |
Thrombophilia + |
|
Detected 6 variables on 4 genes: - MTHFR: C677T, A1298C - F2: G20210A (Prothrombin FII) - F5: G1691A (FV Leiden); A4070G (FVR2) - PAI-1: Separin PAI-1 4G/5G
|
Detected 13 variables on 11 genes - MTHFR: C677T, A1298C - F2: G20210A (Prothrombin FII) - F5: G1691A (FV Leiden); A4070G (FVR2) - PAI-1: Separin PAI-1 4G/5G - F7: G10967A (Arg353Gln) - F13A1 (FXIII): G103T (Val34Leu) - ITGA2: C807T (Phe224Phe) - ITGB3: T1565C (Leu33Pro) - FGB (BF): -455G>A - MTRR: A66G (Ile22Met) - TFPI: C536T (Pro179Gln) |
Sample required: 2ml of whole blood
Method: Genetic sequencing
Turnaround time: 5 days
Sensitivity: 100%
Specificity: 100%
Sources: hosrem.org.vn, vinmec.com
REFERENCES
- ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 197: Inherited Thrombophilias in Pregnancy. Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2018; 132(1): e18-e34.
- Evaluation and treatment of recurrent pregnancy loss: a committee opinion. Fertil Steril. 2012; 98 (5): 1103-1111.
- Ford HB & Schust DJ. Recurrent pregnancy loss: etiology, diagnosis, and therapy. Reviews in obstetrics & gynecology. 2009; 2(2): 76–83.
- No, Green-top Guideline. The investigation and treatment of couples with recurrent first-trimester and second-trimester miscarriage, April 2011.
- Practice Bulletin No. 132: Antiphospholipid syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 2012; 120(6): 1514-1521.
- Rey E et al. Thrombophilic disorders and fetal loss: a meta-analysis, Lancet. 2003; 361(9361): 901-908.
- The ESHRE Guideline Group on RPL. ESHRE guideline: recurrent pregnancy loss, Human Reproduction Open. 2018; (2).

3 types of PGTest tests commonly used today
PGT-A (Preimplantation Genetic Screening for Aneuploidy)
PGT-A is a preimplantation genetic analysis test that helps detect abnormalities in the number of chromosomes in the embryo. Chromosomes are genetic materials containing DNA. The number of each type of human’s chromosome is 2. When the number of chromosomes changes, it can impede the embryo from developing, consequently failing to be implanted in the uterus, or can cause Down, Turner, Klinefelter Syndrome,...

PGT-SR (Preimplantation Genetic testing for structural chromosomal rearrangements)
PGT-SR is an evaluation test for abnormalities caused by chromosomal restructuring. The PGT-SR test can detect chromosomal abnormalities caused by non-reciprocal translocation, Robertsonian translocation and inversions.
PGT-M (Preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic/single gene defects)
PGT-M is a preimplantation genetic analysis test that detects diseases due to single-gene disorders.
In which circumstance should the PGTEst be applied?
PGT-A
PGT-A is a preimplantation genetic test aiming at identifying aneuploidy abnormalities, which can be deployed to screen aneuploidy types relating to any chromosome. PGT-A should be commonly indicated to:
- Expectant mothers aged > 37 years old.
- Multiple IVF failures or successive miscarriages.
- Family history of children born with quantitative abnormalities of chromosomes.
- The husband is diagnosed with severe infertility (AZF deletion).
.png)
PGT-SR
PGT-SR is often applied to couples with chromosomal structural abnormalities such as chromosomal non-reciprocal translocation, chromosomal deletion or duplication.
In case one or both parents have syndromes related to chromosomal structural abnormalities such as: Angelman, Cri du chat, DiGeorge, Langer – Giedion, Miller – Dieker, Prader – Willi, Smith – Magenis, Williams – Beuren, Wolf – Hirschhorn...
PGT-M
Spouses carry genetic mutations that cause diseases: Thalassemia, Myeloid atrophy, cystic fibrosis,...
The wife carries the sex chromosome X-linked gene mutation (Hemophilia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy...)
PGT-M is a diagnostic test for monogenic diseases that is often recommended for cases such as parent or both parents carrying monogenic genetic mutations such as chromosomal disorders, congenital hemolytic disease Thalassemia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, etc.
Reasons that couples should take the PGTest test
Increase in the success rate per transfer attempt: Choosing embryos that do not have an abnormal number of chromosomes can increase the pregnancy rate after embryo transfer.
Reduction in miscarriage rate: In the general population, 25% of all clinical pregnancies end in miscarriage. The risk of miscarriage will be reduced if the embryo does not have an abnormal number of chromosomes (euploids) transferred.
Reduction in the risk of multiple pregnancies: Patients can confidently transfer an embryo that has been tested for chromosomes and not have an abnormal number of embryos instead of transferring multiple embryos that have not been tested for chromosomes, which reduces the risk of multiple pregnancies.
Increase the likelihood of having a healthy baby: Some pregnancies with aneuploid fetus can lead to the baby being affected in relation to chromosomal syndromes (e.g. Down syndrome).
Less time and resources needed: The time and resources required to achieve a pregnancy are reduced.
GENTIS - The agency that performs accurate and reputable PGTest testing
GENTIS with more than 13 years of operation in the field of obstetric-assisted testing is considered capable of performing PGTest testing techniques accurately and professionally.
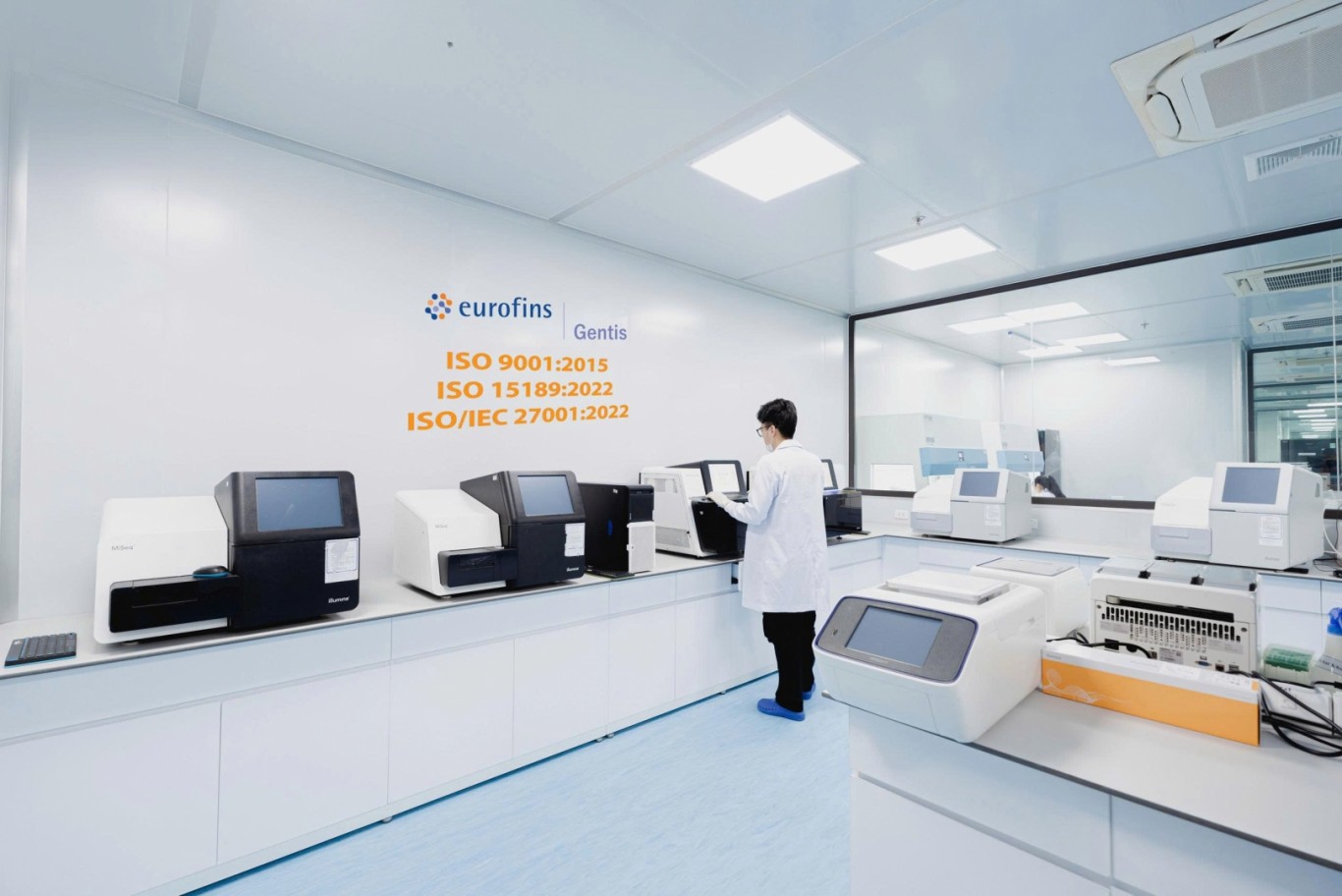
GENTIS testing center is strongly invested in facilities, modern equipment systems, imported from famous technology companies in the world. The entire operation process of GENTIS Testing Center is accredited by ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 15189:2012 standards.
.jpg)
At GENTIS, we gather a team of highly specialized experts, doctors, and technicians with many years of experience in the field of assisted reproduction and especially in the technique of performing PGTest tests.
With the desire to improve the health quality of Vietnamese people, GENTIS always tries day by day, to actively improve service quality, and diversify reproductive support products to serve the community. GENTIS hopes to bring more good news to infertile couples looking for children.
The scientific paper was carried out by Pham Dinh Minh, PhD., Nguyen Thi Kieu Oanh, MSc., Nguyen Thi Huyen, MSc. MD (GENTIS Genetic Analysis Services JSC), and Dang Thi Nga, MSc.MD. (University of Public Health). The research was conducted from January 2023 to May 2023 at the GENTIS Testing Center.

After a three-month approval process, the paper was published in the Vietnam Medical Journal on August 30, 2023. This prestigious journal is highly regarded and widely read both within and outside the medical community.
Congenital metabolic disorders are rare genetic conditions in children caused by deficiencies in receptors, enzymes, transport proteins, or co-factors in the metabolism of amino acids, fatty acids, and organic acids. This leads to abnormal changes in the synthesis or degradation pathways of substances in the body, resulting in toxic products that cause cytotoxicity and impair organs’ functions.
Metabolic disorders often go undetected due to the lack of clear symptoms in the early stages of a newborn's development. Consequently, when clinical symptoms appear, it is often too late, leading to mild to severe neurological dysfunctions, developmental delays, and even death.
Therefore, newborn screening for metabolic disorders is crucial for early diagnosis, timely treatment, improving quality of life for patients, and reducing burdens on families. Advances in mass spectrometry technology, particularly tandem mass spectrometry (MSMS), have made screening more affordable, sensitive, and specific. The Neobase 2 kit running on the XEVO TQD system based on the MSMS technique uses dried blood spots from heel pricks to screen for multiple metabolic disorders quickly and accurately.
The XEVO TQD liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry system by Waters is IVD-certified, offering high reliability, sensitivity in monitoring MRM transitions, rapid switch rates, and cost efficiency for laboratories. The NeoBase 2 Non-derivatized MSMS kit by Perkin Elmer can screen for 77 different congenital metabolic disorders. Before integrating the kit into screening for metabolic disorders on the XEVO TQD, method validation is required. Thus, aim of the study is: “Applying CLSI's NBS04 guideline in validating the method for quantifying some amino acids and acylcarnitines on dried heel blood samples using the NeoBase 2 kit on the XEVO TQD machine.”

The XEVO TQD liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry system by Waters is IVD-certified, offering high reliability
The report by GENTIS and the University of Public Health demonstrated that the MSMS method for analyzing amino acids and acylcarnitines using the Neobase-2 kit on the Xevo TQD system provides acceptable linearity, precision, and accuracy, ensuring reliability for neonatal screening services.
“A Verification method in Newborns Screening of Metabolic Disorders by the NEOBASE 2 MSMS KIT using XEVO TQD” is a significant scientific achievement contributed by the R&D team at GENTIS and experts at the University of Public Health to the national medical field. Particularly, the MSMS method for screening congenital metabolic disorders has proven accurate and reliable under the practical conditions of the GENTIS Testing Center, supporting clinical practices in screening various congenital metabolic disorders.
Sharing about this achievement, Pham Dinh Minh, PhD. said: “GENTIS prioritizes ensuring the highest quality of tests. Therefore, validating methods before introducing new equipment is indispensable.”
With the desire to contribute more to the development of the national medical field, GENTIS will strive to conduct more research, bringing quality and meaningful scientific papers in the future.
Read the full scientific paper published in the Vietnam Medical Journal here:
https://tapchiyhocvietnam.vn/index.php/vmj/article/view/6528/5834
GENTIS 13th Anniversary: Strong Foundation - Breakthrough together
GENTIS is the official partner of the 1st Regional Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Diagnostic Screening in North-Central Vietnam
GENTIS is honored to be the Silver Sponsor of the 1st North Central Region Conference on Prenatal and Neonatal Screening and Diagnosis
GENTIS - The Main Sponsor of the ACP 2023 Annual Scientific Conference
GENTIS is honored to be the Main Sponsor of the 2023 National Scientific Conference of the Vietnam Medical Genetics Association.
Understanding Thrombophilia and Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
3 commonly used preimplantation genetic analysis tests or PGTest
New Study on Confirming Congenital Metabolic Disorder Screening Method by GENTIS and the University of Public Health Published in the Vietnam Medical Journal
Please fill in the information below to receive our supports and consultations!
Please fill in the information below to receive our supports and consultations!





-360x194.png)